
Protracted Time - How old is time? Are rocks your best chronometer? What is the "correct" reference angle to view time? Can you freeze time? Is there quality to time? Is mechanistic physics capable of explaining time? Does time have negative, zero or infinite expressions? Relativistic and Quantum Physics is sure time is not a reliable static construction.
Which rock or view in these pictures makes geologic time make since?
Time is a derivative, not primary or causal. Do not focus on it.

When walking I stop to view rocks. They have a story to tell, if only we knew what. I am retired and no longer carry a phone or watch. As it happens the impact of the large meteor I study makes a pulsing picture in it's reforming outline. Event sequence is my referencing. Length, width, time are only measures with standard increments. You cannot calibrate radioactive decay over millions of years. Will you trust your soul, your eternal spirit to the only verifiable Person, God or the guess makers who don't know why you are?

Looking up and down.
The heaven above
and hell below
so what do we know?
You know what you seek to know.
If you seek to understand you crawled up as a worm you won't belong in heaven you will learn.
If you are from heaven above, a place of love, is there you will return.
Skepticism is the foundation of so called "modern" science. They are correct that you should be a skeptic of what they preach. Consider how easy it is to debunk the very foundation of what they say about evolution and it's base, old earth fossil geology.
Light as time? The visible universe. God Challenges Job
…18Have you surveyed the extent of the earth? Tell Me, if you know all this. 19Where is the way to the home of light? Do you know where darkness resides, 20so you can lead it back to its border? Do you know the paths to its home?


50 years ago when I was taught the mechanistic Newtonian sciences the direction of order to disorder was a universal truth. Good news there, it gives mechanics and engineers jobs, LOL. But alas so called science isn't. It is a social club of popularity and this concept is now amended to please the conflicting theory of evolution members. 50 years ago they had less clout since the world had suffered so much at the hands of their Nazi master race survival of the fittest evolution believers. I have not observed any evolution and the laundry only makes tangles.
While you cannot validate "old earth" 4.5 billion year protracted time with rocks, as there is no way to demonstrate confirmation, you can confirm in historic time species disappearance and no appearance. This is consistent with the mechanistic physical law of order to disorder i.e. validation. Finding fossil ape/man like bones only indicates an ape like creature species disappeared or dis ape appeared. While no species has been observed to appear they are being altered or "engineered." While it really does not matter if you believe the earth to be 4.5 billion years old; it does matter if you believe in God as your creator. Life and the ability to believe do not evolve and will never be made in a lab or any random process.
Space time as a pattern of ejecta - Study of the Howell/Petersburg impact phenomena shows a chaos field and multi ejecta types, speeds and distributions. Time and velocity being relativistic. Much of the shock being hyper velocities beyond knowing. When the universe is studied same is true. Can't find a constant expansion velocity.
Space time as a pattern of ejecta - Study of the Howell/Petersburg impact phenomena, oh that part of same discussion is just catching up again. Check out this youtube video on the problem of universal expansion time. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jiSwvxA5v4Q
So what is the difference between rock geology and fossil geology? By study of the area I was able to put together what happened. The tools of the previous investigators do not work. The faults are ignored a fatal mistake in reconstruction. Fossils strata study confuses them because the shock melts the strata dropping fossils in a metamorphic liquid soup. The iron they assume is just there for no reasonable cause. And alas time. Time does not exist in a blast zone. The meteor itself could have been traveling 30 miles per second. Relativity would even start to apply for matter in this impact. Basically Middle, TN was reorganized in minutes not millions of years. As a test I submitted a fossil for identification to the highest TN authority. I am sure he was completely wrong about the rock and pretty sure the fossil identification was also wrong. So over time from reading the early studies I can tell that geology in TN has declined over time like order to disorder even though it is a highly invested program. The high point of TN geology was in the 1960's. They got a couple of craters identified and had mapped a lot of TN and even more important were nice.
Earth
<<<<< Howell/Petersburg a counter rotator making earth day longer.
Is the Howell/Petersburg event an impact or sideswipe? Take a look at the fault pattern below. It does not look like a compressive slowing down. The faults are equally spaced. This could be a divot from a planet sized object!
The Howell/Petersburg impact flooded over 100 miles around with radiation making carbon dating unreliable. So with 16,000 earth hits there would be others.
Creation sequence as Bible issue: https://www.kjvbible.org/thedebate.html
The complex way we perceive a day.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IJhgZBn-LHg

Strata is a vertical layering idea, right?

Time and reality and the Webster Springs West Virginia Crater. A rock identification post alerted me to a crater in West Virginia. Does the crater exist? Well certainly nobody is aware of it except myself and I am not sure what the specimen owner thinks. From the wood grain going around a knot folding pattern of the tectonic faults when the Appalachian mountains were forming I can see the crater. This would make it early Ordovician. So it exist for me. But mine in this case is not a shared reality. It does not exist for others. Even more, quantum existence says that all matter is only a waveform of undetermined possibilities unless conscious awareness causes it's particles to take a fixed point. So that awareness is just typical mountain to everybody but me when observed. But hey, I will never go there. It's reality is just an idea. And time does not even exist one way or the other. Is like prequelism https://www.hillbillyu.com/prequil-ism
Time, motion, music & dance.
While time is not the primary causality, events are; you can relate it to music and dance. They exist as relational to each other.
Beyond that you have to have consciousness.
If you freeze all events Time still exist for consciousness which notes that nothing is moving. Absent consciousness time is not.

The Twilight Zone and Time - 60 years ago there was a show called The Twilight Zone with interesting thought provoking stories. It started with the screen showing static and the host Rod Serling saying don't adjust your set. Well later some guys won the Noble Prize by claiming the static on your TV set is light from the Big Bang that has decayed into electromagnetic waves.
So if light is the fastest speed how can we be here receiving that record? By definition that signal would be far ahead of any matter which would follow the light.
And speaking of event and sequence, what if the solar system was stationary. What would be your clock? The rotation is an event, not time.

Solar time - We use a modification called Mean Solar Time which organizes an area into the same time zone. So it is not solar time which would vary from place to place. Now the year varies in daylight due to all the rotation effects but comes back to the same place which would be a journey that went nowhere like Deja Vu all over again. So if time is an event based mechanical structure and you cycle back in an endless loop it is a non event and therefore non time. Zero, or a quality of zero.
the point event - there is a depth to experience of any event. your perspective and width of observation. Only god can completely record or witness any event.
the premise of science that observing and repeating events is a point reference with universal limitation.
The time hole. I am not a fan of rock dating. When asked when Collide Clyde the Bolide hit here in lower Middle TN. I say it was the last geological event, as there are only impacted rocks here. But let's compare spheres for reference. The hollow sphere is from a crater believed to be almost a half billion years old. The shinny one is from here. So you can tell old and new in a relational way.



The assumption that it takes millions of years for inches of rock to form is documented how?
.jpg)
It is thought that physics does not exist in the early big bang and certainly the pre big bang. Well that is just mistaken. The overarching phenomena of physics is kinetic i.e. motion. All other physics are subordinate. Kinetic physics even proceeds the big bang as thought has movement. Mind exist kinetically and is outside and inside the universe. Time is event dependent and is not bound by the universe. The reports of those who visit Heaven indicate time dilation.
Does time even agree with its self? No. Consider the progress and regression. Time as a dependent to movement would add and subtract and not record what is thought of as time. Mind time does not have to agree with physical movement or any other mind. Does Quantum Physics have a relational problem connecting with Mind Time? Mind Time is multi function and does not have to even connect with its self. Constrained time is bounded to: events, direction, task, ... (kinetic constructs). Break throughs are not time like movement but disconnected jumps. Take a look at the clock below. It is more like the break through than any connected time clock.


Fabric weave forensic system resonance - A multitude of forces extend through the universe as a progression. Light, gravity, shock, ..., these forces combine as a multiple sum resonance as if you strike a drum head with many objects.

The system has no one event source but contains the crossing of event source energies entangled. While having a single point source, a slice of the universe in progression is not a single event picture and is a summation and not time referenceable.
_JPG.jpg)
Specimen collected on back side of Frankewing, TN Crater Wall in NW Giles, County, TN. It is a shock made conglomerate although with a fine matrix of blast particles. The surface is growing mycelium in an expansion. As forensic evidence it is events in motion but disjointed.

Wave interaction and system harmonics - No one force defines systems and a system is seeking a stable combination called the system harmonic. At any point in the system it will be in some state of balance seeking or a sub harmonic. Calculating time from complex motion is problematic.

The gravity constant - The gravity constant assumes linearity. While easier to calculate it is a poor assumption as very little is linear. It is how dark matter was presumed to exist. In fact gravity changes at its margins significantly and no dark matter is needed to explain the forces. Gravity is a wave and time is mutable.
Force of Gravity Formula
The formula to calculate the gravitational force is
F = GmM/r2 or GmMd2
Where,
d is the distance between the two objects.
m is the mass of object 1 in kg.
M is the mass of object 2 in kg.
G is the gravitational constant value which is 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 / kg2.
r is the radius.
d is the distance between the objects.

Fundamentally wrong - Oldest meteorite ever found is based on tectonic assumption. The surface indicates it was clearly formed in an impact explosion as you can see from the shock particle storm surface. It even has a fractal to circle constellationing effect (circled). You can read the bogus article at: http://www.meteoritestudies.com/EC002AMb.jpg
Is this even a meteorite? No cavitation, no melt direction flow yet obvious melt and cooling cracks. The rivulet pattern is not pronounced as it has a climbing fractal to circle pattern which is unlikely in an atmosphere entry. Actually counter to surface melt from atmospheric entry.

-
If ∂2y/∂x2 > 0, the slope increases, the function bends upward and the acceleration is directed upward.
-
If ∂2y/∂x2 < 0, the slope decreases, the function bends downward and the acceleration is directed downward.
-
If ∂2y/∂x2 = 0, the slope is constant, the function is straight at that point and the acceleration is null.
How far to someplace? Distance as time? The journey of a harmonic is not linear. A system of harmonics will arrive at many times. From: Waves (scientificsentence.net)
Physics Mystery Solved: Findings Could “Revolutionize” Our Understanding of Distance
TOPICS:Particle PhysicsPopularPurdue UniversityQuantum Physics
By PURDUE UNIVERSITY JULY 26, 2022
The researchers discovered that a new theoretical framework to unify Hermitian and non-Hermitian physics is established by the duality between non-Hermiticity and curved spaces.
A physics puzzle is resolved through a new duality.
According to traditional thinking, distorting a flat space by bending it or stretching it is necessary to create a curved space. A group of scientists at Purdue University has developed a new technique for making curved spaces that also provides the answer to a physics mystery. The team has developed a method using non-Hermiticity, which occurs in all systems coupled to environments, to build a hyperbolic surface and a number of other prototypical curved spaces without causing any physical distortions of physical systems.
“Our work may revolutionize the general public’s understanding of curvatures and distance,” says Qi Zhou, Professor of Physics and Astronomy.

linear approximate - This is what is common to much of daily usage. Really more like a collection of different waves traveling over a non flat surface.

So the meteor bolide protoplanet that struck here and made a progressive sliding crater left the various relics of different time formation and event types which I study. The shock wave was so powerful it left earth went out into space and is still traveling as part of the same impact event. The impact event continuum it traces back to the big bang and moves between matter, energy and motion. However it inter relates with the entire system. Your time to a distance is different depending on the weather.
Now look below at the presumed journey of the cat family. Assumed divergence is not as logical as wave travel. You would have a variable off a mean depending on the type of terrain, but they would all be cats and the DNA all complex and adaptive not evolution.
The "common ancestor theory is not compatible with common wave theory as the most observed natural phenomena. Complex is. Complex is not a journey. Why would they have to have a common ancestor? What we actually observe in historical nature is extinction of high diversity as a record of previous higher and higher diversity. The assumption of a simple architecture is an imposed evolutionary model. Fossil theory is a very poor science. Most fossils I have observed and studied were made in a catastrophic event and do not represent any typical situation.

Nor are fossils presented as how found or in situ. You get some artist extrapolation bias as they are paid by evolutionist.


Not a bad reconstruction, of course spots are conjecture. It is basically like a modern big cat and the assumption is early cats continue but you had species diverge somehow. This assumption is counter to evidence as you have clear DNA evidence that make a complex separate distinctiveness.
The universe being complex and distributed as many wave functions is more valid.
Furthermore man is supposed to originate in Africa why would an origin wave differ?
Fossil samples are a catch as catch can not a true sample but what you do have is the earliest sample is modern and complex which supports original complex and wave dispersal.

Panthera blytheae: Oldest Big Cat Fossil Found in Tibet
Nov 14, 2013 by Natali Anderson
|
A well-preserved 6 to 4 million-year-old skull of a previously unknown species of prehistoric snow leopard from Tibet is the oldest big cat fossil ever found, according to paleontologists from China, Canada and the United States.
Life reconstruction of Panthera blytheae. Image credit: Mauricio Antón.
“This find suggests that big cats have a deeper evolutionary origin than previously suspected,” said Dr Jack Tseng from the American Museum of Natural History in New York, who is the lead author of a paper reporting the discovery in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
DNA evidence suggested that the Pantherinae subfamily, including lions, jaguars, tigers, leopards, snow leopards and clouded leopards (so-called big cats), diverged from their nearest evolutionary cousins, Felinae, which included cougars, lynxes and domestic cats, about 6.37 million years ago.
However, the oldest fossils of big cats previously found were 3.6-million-year-old tooth fragments uncovered at Laetoli in Tanzania by Mary Leakey in the 1970s.
The newly found skull fossil is important because it partially fills the gap.
Dr Tseng’s team unearthed it in 2010 while scouting in the remote border region between Pakistan and China, an area that takes a bumpy seven-day car ride to reach from Beijing.
Skull of Panthera blytheae. Image credit: Tseng ZJ et al.
The scientists found more than 100 bones that were likely deposited by a river eroding out of a cliff. There, below the antelope limbs and jaws, was the crushed but largely complete skull of a big cat.
For the past three years, Dr Tseng and his colleagues have used both anatomical and DNA data to determine that the skull does, in fact, represent a new species, named Panthera blytheae.
“The species name, blytheae, honors Blythe, the snow-leopard-loving daughter of Paul and Heather Haaga, who are avid supporters of the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.”
Using magnetostratigraphy, the paleontologists were able to estimate the age of the Panthera blytheae‘s skull at between 4.10 and 5.95 million years old.
The discovery not only challenges previous suppositions about the evolution of big cats, it also helps place that evolution in a geographical context.
Biogeographic evolution of big cats. Image credit: Tseng ZJ et al.
Panthera blytheae was found in a region that overlaps the majority of current big cat habitats and suggested that the group evolved in central Asia and spread outward.
In addition, recent studies suggested that the genus Panthera did not split from genus Neofelis (clouded leopards) until 3.72 million years ago – which the new find disproves.
______
Bibliographic information: Tseng ZJ et al. 2013. Himalayan fossils of the oldest known pantherine establish ancient origin of big cats. Proc. R. Soc. B, vol. 281, no. 1774; doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.2686
From Sci News at: Panthera blytheae: Oldest Big Cat Fossil Found in Tibet | Paleontology | Sci-News.com



The black hole is spinning faster than light, hence black. It has an oscillation which spins the photons out on a loop. As photons are an energy crystal body (energy/mass cusp) they are able to interact.
Thomas Lewton
September 8, 2022
hen photons hurtle toward a black hole, most are sucked into its depths, never to return, or gently deflected away. A rare few, however, skirt the hole, making a series of abrupt U-turns. Some of these photons keep circling the black hole practically forever.
Described by astrophysicists as a “cosmic movie camera” and an “infinite light trap,” the resulting ring of orbiting photons is among the weirdest phenomena in nature. If you detect the photons, “you’re going to see every object in the universe infinitely many times,” said Sam Gralla, a physicist at the University of Arizona.
But unlike the iconic event horizon of a black hole — the boundary within which gravity is so strong that nothing can escape — the photon ring, which orbits the hole farther away, has never received much attention from theorists. It makes sense that researchers have been preoccupied with the event horizon, since it marks the edge of their knowledge about the universe. Throughout most of the cosmos, gravity tracks with curves in space and time as described by Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity. But space-time warps so much inside black holes that general relativity breaks down there. Quantum gravity theorists seeking a truer, quantum description of gravity have therefore looked to the horizon for answers.
“I had taken the view that the event horizon was what we needed to understand,” said Andrew Strominger, a leading black hole and quantum gravity theorist at Harvard University. “And I thought of the photon ring as some sort of technical, complicated thing which didn’t have any deep significance.”
Now Strominger is making his own U-turn and trying to convince other theorists to join him. “We’re exploring, excitedly, the possibility that the photon ring is the thing that you have to understand to unlock the secrets of Kerr black holes,” he said, referring to the kind of spinning black holes created when stars die and gravitationally collapse. (The photon ring forms concurrently.)
In a paper posted online in May and recently accepted for publication in Classical Quantum Gravity, Strominger and his collaborators revealed that the photon ring around a spinning black hole has an unexpected kind of symmetry — a way that it can be transformed and still stay the same. The symmetry suggests that the ring may encode information about the hole’s quantum structure. “This symmetry smells like something to do with the central problem of understanding the quantum dynamics of black holes,” he said. The discovery has led researchers to debate whether the photon ring might even be part of a black hole’s “holographic dual” — a quantum system that’s exactly equivalent to the black hole itself, and which the black hole can be thought of as emerging out of like a hologram.
“It opens up a very interesting avenue for understanding the holography of these [black hole] geometries,” said Alex Maloney, a theorist at McGill University in Canada who was not involved in the research. “The new symmetry organizes the structure of black holes far from the event horizon, and I think that’s very exciting.”
Photons that make a single U-turn around a black hole before flying away from it create an image of a ring, labeled n = 1 in the video. Photons that redirect twice before flying away from the hole form an image of a thinner ring within the first ring, labeled n = 2 in the video, and so on.
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
Much more theoretical study is needed before researchers can say for sure whether, or in what way, the photon ring encodes a black hole’s inner contents. But at the very least, theorists say the new paper has detailed a precise test for any quantum system claiming to be the black hole’s holographic dual. “It’s a target for a holographic description,” said Juan Maldacena of the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, one of the original architects of holography.
Hiding in the Photon Ring
Part of the excitement about the photon ring is that, unlike the event horizon, it’s actually visible. In fact, Strominger’s U-turn toward these rings happened because of a photograph: the first-ever image of a black hole. When the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) unveiled it in 2019, “I cried,” he said. “It’s amazingly beautiful.”
Elation soon spiraled into confusion. The black hole in the image had a thick ring of light around it, but physicists on the EHT team didn’t know whether this light was the product of the hole’s chaotic surrounding environment, or if it included the black hole’s photon ring. They went to Strominger and his theorist colleagues for help interpreting the image. Together, they browsed the huge databank of computer simulations that the EHT team was using to disentangle the physical processes that produce light around black holes. In these simulated images, they could see the thin, bright ring embedded in the larger, fuzzier orange doughnut of light.
“When you look at all the simulations, you can’t miss it,” said Shahar Hadar of the University of Haifa in Israel, who collaborated with Strominger and the EHT physicists on the research while at Harvard. The formation of the photon ring seems to be a “universal effect” that happens around all black holes, Hadar said.
Unlike the maelstrom of energetic colliding particles and fields that surrounds black holes, the theorists determined, the sharp line of the photon ring carries direct information about the black hole’s properties, including its mass and amount of spin. “It’s definitely the most beautiful and compelling way to really see the black hole,” said Strominger.
A global network of radio telescopes known as the Event Horizon Telescope released this first-ever photo of a black hole in 2019 — the supermassive one at the center of the nearby galaxy Messier 87.
Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration
The collaboration of astronomers, simulators and theorists found that the EHT’s actual photograph, which shows the black hole at the center of the nearby galaxy Messier 87, isn’t sharp enough to resolve the photon ring, although it isn’t far off. They argued in a 2020 paper that future, higher-resolution telescopes should easily see photon rings. (A new paper claims to have found the ring in the EHT’s 2019 image by applying an algorithm to remove layers from the original data, but the claim has been met with skepticism.)
Still, having stared at photon rings for so long in the simulations, Strominger and his colleagues began to wonder if their form hinted at an even deeper meaning.
A Surprising Symmetry
Photons that make a single U-turn around a black hole and then zip toward Earth would appear to us as a single ring of light. Photons that make two U-turns around the hole appear as a fainter, thinner subring within the first ring. And photons that make three U-turns appear as a subring within that subring, and so on, creating nested rings, each fainter and thinner than the last.
Light from the inner subrings has made more orbits and was therefore captured before the light from outer subrings, resulting in a series of time-delayed snapshots of the surrounding universe. “Together, the set of subrings are akin to the frames of a movie, capturing the history of the visible universe as seen from the black hole,” the collaboration wrote in the 2020 paper.
Strominger said that when he and his collaborators looked at the EHT pictures, “we were like: ‘Hey, there’s an infinite number of copies of the universe right there at that screen? Couldn’t that be where the holographic dual lives?’”
The researchers realized that the ring’s concentric structure is suggestive of a group of symmetries called conformal symmetry. A system that has conformal symmetry exhibits “scale invariance,” meaning it looks the same when you zoom in or out. In this case, each photon subring is an exact, demagnified copy of the previous subring. Moreover, a conformally symmetric system stays the same when translated forward or backward in time and when all spatial coordinates are inverted, shifted and then inverted again.
Saying conformal symmetry and black hole in the same sentence to a quantum gravity theorist is like waving red meat in front of a dog.
Andrew Strominger, Harvard University
Strominger encountered conformal symmetry in the 1990s when it turned up in a special kind of five-dimensional black hole he was studying. By precisely understanding the details of this symmetry, he and Cumrun Vafa found a novel way to connect general relativity to the quantum world, at least inside these extreme kinds of black holes. They imagined cutting out the black hole and replacing its event horizon with what they called a holographic plate, a surface containing a quantum system of particles that respect conformal symmetry. They showed that the system’s properties correspond to properties of the black hole, as if the black hole is a higher-dimensional hologram of the conformal quantum system. In this way, they built a bridge between the description of a black hole according to general relativity and its quantum mechanical description.
In 1997, Maldacena extended this same holographic principle to an entire toy universe. He discovered a “universe in a bottle,” in which a conformally symmetric quantum system living on the bottle’s surface exactly mapped onto properties of space-time and gravity in the bottle’s interior. It was as if the interior was a “universe” that projected from its lower-dimensional surface like a hologram.
The discovery led many theorists to believe that the real universe is a hologram. The hitch is that Maldacena’s universe in a bottle differs from our own. It’s filled with a type of space-time that’s negatively curved, which gives it a surface-like outer boundary. Our universe is thought to be flat, and theorists have little idea what the holographic dual of flat space-time looks like. “We need to get back to the real world, while taking inspiration from what we learned from these hypothetical worlds,” Strominger said.
And so the group decided to study a realistic spinning black hole sitting in flat space-time, like those photographed by the Event Horizon Telescope. “The first questions to ask are: Where does the holographic dual live? And what are the symmetries?” said Hadar.
Searching for the Holographic Dual
Historically, conformal symmetry has proved a trustworthy guide in the search for quantum systems that holographically map onto systems with gravity. “Saying conformal symmetry and black hole in the same sentence to a quantum gravity theorist is like waving red meat in front of a dog,” said Strominger.
Starting from the description of spinning black holes in general relativity, called the Kerr metric, the group began to look for hints of conformal symmetry. They imagined hitting the black hole with a hammer to make it ring like a bell. These slowly fading vibrations are like the gravitational waves created when, say, two black holes collide. The black hole will ring with some resonant frequencies that depend on the shape of space-time (that is, on the Kerr metric) just as the ringing tones of a bell depend on its shape.
Andrew Strominger and colleagues recently discovered that a black hole’s photon ring has the kind of symmetry that often arises when an object — in this case, the black hole — can be described as a hologram.
Allie Humenuk for Collapsar Films
Figuring out the exact pattern of vibrations is unfeasible because the Kerr metric is so complicated. So the team approximated the pattern by only considering high-frequency vibrations, which result from hitting the black hole very hard. They noticed a relationship between the pattern of waves at these high energies and the structure of the black hole’s photon rings. The pattern “turns out to be completely governed by the photon ring,” said Alex Lupsasca of the Vanderbilt Initiative for Gravity, Waves and Fluids in Tennessee, who co-authored the new paper with Strominger, Hadar and Daniel Kapec of Harvard.
A pivotal moment came in the summer of 2020 during the Covid-19 pandemic. Blackboards and benches were set up on the grass outside Harvard’s Jefferson physics lab, and the researchers could finally meet up in person. They worked out that, like the conformal symmetry which relates each photon ring to the next subring, the successive tones of a ringing black hole are related to each other by conformal symmetry. This relationship between the photon rings and the black hole vibrations could be a “harbinger” of holography, said Strominger.
Another clue that the photon ring may hold special significance comes from the counterintuitive way the ring relates to the black hole’s geometry. “It’s very, very weird,” Hadar said. “As you move along different points on the photon ring, you are actually probing different radii” or depths into the black hole.
These findings imply to Strominger that the photon ring, rather than the event horizon, is a “natural candidate” for part of the holographic plate of a spinning black hole.
If so, there may be a new way to picture what happens to information about objects that fall into black holes — a long-standing mystery known as the black hole information paradox. Recent calculations indicate that this information is somehow preserved by the universe as a black hole slowly evaporates. Strominger now speculates that the information might be stored in the holographic plate. “Perhaps information doesn’t really fall into the black hole, but it sort of stays in a cloud around outside the black hole, which probably extends to the photon ring,” he said. “But we don’t understand how it’s coded in there, or exactly how that works.”
A Call to Theorists
Strominger and company’s hunch that the holographic dual lives in or around the photon ring has been met with skepticism by some quantum gravity theorists, who see it as too bold an extrapolation from the ring’s conformal symmetry. “Where the holographic dual lives is a much deeper question than: What is the symmetry?” said Daniel Harlow, a quantum gravity and black hole theorist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Although he is in favor of further research on the issue, Harlow stresses that a convincing holographic duality, in this case, must show how the properties of the photon ring, such as individual photons’ orbits and frequencies, mathematically map onto the fine-grained quantum details of the black hole.
Nevertheless, several experts said that the new research offers a useful needle that any proposed holographic dual must thread: The dual must be able to encode the unusual vibration pattern of a spinning black hole after it has been struck like a bell. “Demanding the quantum system that describes the black hole reproduces all of that complexity is an incredibly powerful constraint — and one that we’ve never tried to exploit before,” said Strominger. Eva Silverstein, a theoretical physicist at Stanford University, said, “It seems like a very nice piece of theoretical data for people to try to reproduce when attempting a holographic dual description.”
Maldacena agreed, saying, “One would like to understand how to incorporate this into a holographic dual. So it will probably stimulate some research in that direction.”
Maloney suspects that the newfound symmetry of the photon ring will spur interest among both theorists and observers. If hoped-for upgrades to the Event Horizon Telescope get funded, it could start to detect photon rings within a few years.
Future measurements of these rings won’t directly test holography, though — rather, the data will allow extreme tests of general relativity near black holes. It’s up to theorists to determine with pen-and-paper calculations if the structure of the infinite light traps around black holes can mathematically encrypt the secrets within.
The Quanta Newsletter

Every time you see some explanation of frozen dunes turned to rock ask yourself how that would happen? Grains of anything will not support that shape through the sedimentary process. Even if it is supposed that on Mars would have ice filled dunes that process would indicate it happened suddenly and therefore reverse suddenly. If it did not reverse the high winds of Mars would degrade the dune shape by abrasion.
Ray Forage · September 11, 2022 ·
I have Durness on my list but for geology reasons: this is a bonus. A beach near Durness on the coast of the Northwest Highlands
Credit Shirley-anne Steven in a reply in Highland Scenery.

The prehistory? This is a 5,000 BC village in Czechoslovakia which is far north of the previously known civilizations.
The so-called roundel, built around 7,000 years ago, is located in the district of Vinoř on the outskirts of Prague|Photo: Archaeological Institute of the Academy of Sciences

Everything Astronomy and the Universe ·
Ray Forage · Sept. 24, 2022
Astronomers have found a gas blob orbiting our supermassive black hole at super speed... "We think we're looking at a hot bubble of gas zipping around Sagittarius A* on an orbit similar in size to that of the planet Mercury, but making a full loop in just around 70 minutes," says astrophysicist Maciek Wielgus of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany.
"This requires a velocity of about 30 percent of the speed of light!"
Speed density - This is the construction sequence of a black hole. The orbiting feature will increase in speed and enter the black hole going faster than the speed of light having ultimate density. It is a conversion being made m=E/c^2
Time being a dependent of motion now no longer exist as such and is now a construction of energy in a freeze frame of this mass capture.
Why do Black Holes form? Unrestrained orbit velocity. Terminal velocity is the result of a competing force if there is no such force velocity will keep increasing.
Does velocity keep increasing inside the Black Hole? Mass, Energy and Motion shifts are going to favor Motion as it is the most fundamental universe construction. Therefore Motion will prevail. As the drag of collecting pulls on the Black Hole it will converting Mass to Motion. Energy is also emitting as a conflict with the stress. But time was never a primary one metric it is only an event dependent construct and event is Motion which is captured into this conversion.
As this is not a perfect machine you have motion and energy leakage and the time will progress at relation to motion leakage.
The theory that black holes are made by exploding stars is also used to explain the distribution of heaver matter. So if you accept that you need another mechanism for black holes.

The same event in different sequences. There is a secondary iterative turning motion to very high energies. Oct. 28, 2022
Space.com
X-ray view of wreckage from a star-killing cosmic explosion reveals magnetic surprise
By Robert Lea
published 7 days ago
Using NASA's IXPE space observatory astronomers have mapped polarized X-rays from Cassiopeia A the remains of a massive star that went supernova.
-
Cassiopeia A as imaged by the Chandra X-ray observatory has been investigated in polarized X-rays. (Image credit: NASA/CXC/SAO; IXPE: NASA/MSFC)
The polarization of X-rays coming from the remains of a distant exploded star has been measured and mapped for the first time by astronomers.
The results collected from the stellar wreckage known as Cassiopeia A (Cas A) could shed new light on the nature of young supernova remnants and their magnetic fields, which can accelerate particles to near the speed of light.
The findings represent a new way of reconstructing the explosive death of massive stars as they become supernovas — a process that seeds the universe with elements that become the building blocks of the next generation of stars.
Astronomers collected X-ray data from Cas A — located 11,000 light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia — using the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) space observatory.
The first object that IXPE began observing after its launch in December 2021, Cas A, was selected because the shock waves generated from the supernova that created it are some of the fastest in the Milky Way.
The shockwaves were created when a massive star ran out of fuel for nuclear fusion and could no longer support itself against gravitational collapse. As the core of the star collapsed, it triggered a massive supernova and sent these shockwaves through what was once the star's outer layers.
Light from the destruction of this massive star and the creation of the Cas A stellar wreckage — which is around 29 light-years wide — swept over Earth over 300 years ago.
In the extreme conditions found around supernova remnants like Cas A, magnetic fields grab charged particles like electrons and protons and accelerate them to speeds approaching that of light. These particles are, despite their super-speed, trapped around supernova remnants traveling in curved paths.
When charged particles travel along curved paths at speeds near that of light — or relativistic speeds — they generate an intense form of light called synchrotron radiation. This radiation escapes the supernova remnant across a range of wavelengths of light including low-energy radio waves and high-energy X-rays.
This radiation is polarized by magnetic fields regardless of its wavelength, meaning that encoded within it is information about the magnetic field of the supernova remains from which it originates.
Now, thanks to IXPE data, astronomers can measure this polarization for X-ray light and thus unlock the secrets of the magnetic fields around Cas A.
"Without IXPE, we have been missing crucial information about objects like Cas A," Center for Astrophysics at Harvard & Smithsonian, Pat Slane, who leads the IXPE investigations of supernova remnants, said in a statement(opens in new tab). "This result is teaching us about a fundamental aspect of the debris from this exploded star — the behavior of its magnetic fields."
Studying the polarization of light from Cas A has enabled astronomers to reverse engineer the processes that are occurring within the supernova remnant at small scales. This has allowed them to gather details about Cas A and its magnetic field that are unobtainable in any other way.
Read more: The 'Ghost of Cassiopeia' Drifts Along in This Spooky Hubble Image
Cassiopeia A as imaged by the Chandra X-ray observatory with annotations that mark the polarization vectors of its X-rays as seen by IXPE. (Image credit: Chandra: NASA/CXC/SAO; IXPE: NASA/MSFC)
Reconstructing a star's explosive scene of death
The angle of polarization of the light from a supernova remnant reveals the direction of its magnetic field. Small amounts of polarization indicate that the magnetic fields are close to the leading shockwaves, or shockfront. This is because magnetic fields near a shockfront are tangled and chaotic, oriented in different directions resulting in less polarization.
"These IXPE results were not what we expected, but as scientists, we love being surprised," University of Amsterdam astrophysicist and lead author Jacco Vink said in the statement(opens in new tab). "The fact that a smaller percentage of the X-ray light is polarized is a very interesting — and previously undetected — property of Cas A."
This low polarization implies that X-rays from Cas A are generated in turbulent regions with a mix of many different magnetic field directions.
"This study enshrines all the novelties that IXPE brings to astrophysics," said Riccardo Ferrazzoli, study co-author and researcher at the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics and Institute for Space Astrophysics and Planetology in Rome. "Not only did we obtain information on X-ray polarization properties for the first time for these sources, but we also know how these change in different regions of the supernova.
"As the first target of the IXPE observation campaign, Cas A provided an astrophysical 'laboratory' to test all the techniques and analysis tools that the team has developed in recent years."
Read more: NASA's newly launched X-ray space telescope is ready to start observing the cosmos
An artist's depiction of the IXPE observatory in space. (Image credit: NASA)
Observations of radio wave synchrotron radiation from Cas A with radio telescopes had previously shown that is produced in regions across almost the entire supernova remnant. Only a small amount of these radio waves — about 5% — are polarized. This radio wave data seems to indicate that the magnetic field of Cas A is oriented radially like the spokes of a bike wheel radiating out from its center to its outer rim.
Observations for higher energy X-ray synchrotron radiation taken by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory tell a different story, however. These higher energy emissions seemed to come from thin regions along the shockwaves, near the circular outer rim of Cas A, an area where the magnetic fields are predicted to align with the shocks.
Prior to IXPE, scientists predicted X-ray polarization would be produced by magnetic fields that are aligned at 90 degrees (perpendicular ) to magnetic fields that polarize the radio wave radiation.
IXPE X-ray data suggest instead that the magnetic fields that polarize this high-energy light are aligned radially and are located close to the shockfront. The X-rays from Cas A also seem to possess a lower amount of polarization than even the radio waves.
IXPE will now be used to study other supernova remnants. Astronomers expect each observation to reveal new information about these violent cosmic explosions and the environments they create.
"These results provide a unique view of the environment necessary to accelerate electrons to incredibly high energies," research co-author and University of Amsterdam researcher, Dmitry Prokhorov, said. "We are just at the beginning of this detective story, but so far the IXPE data are providing new leads for us to track down."
The team's research is detailed in a paper posted to the preprint server ArXiv(opens in new tab).

Notice the coning! While the picture shows a tube it is more likely an expanding cone with dimensions unable to see and the tube is a representation of that viewing difficulty.
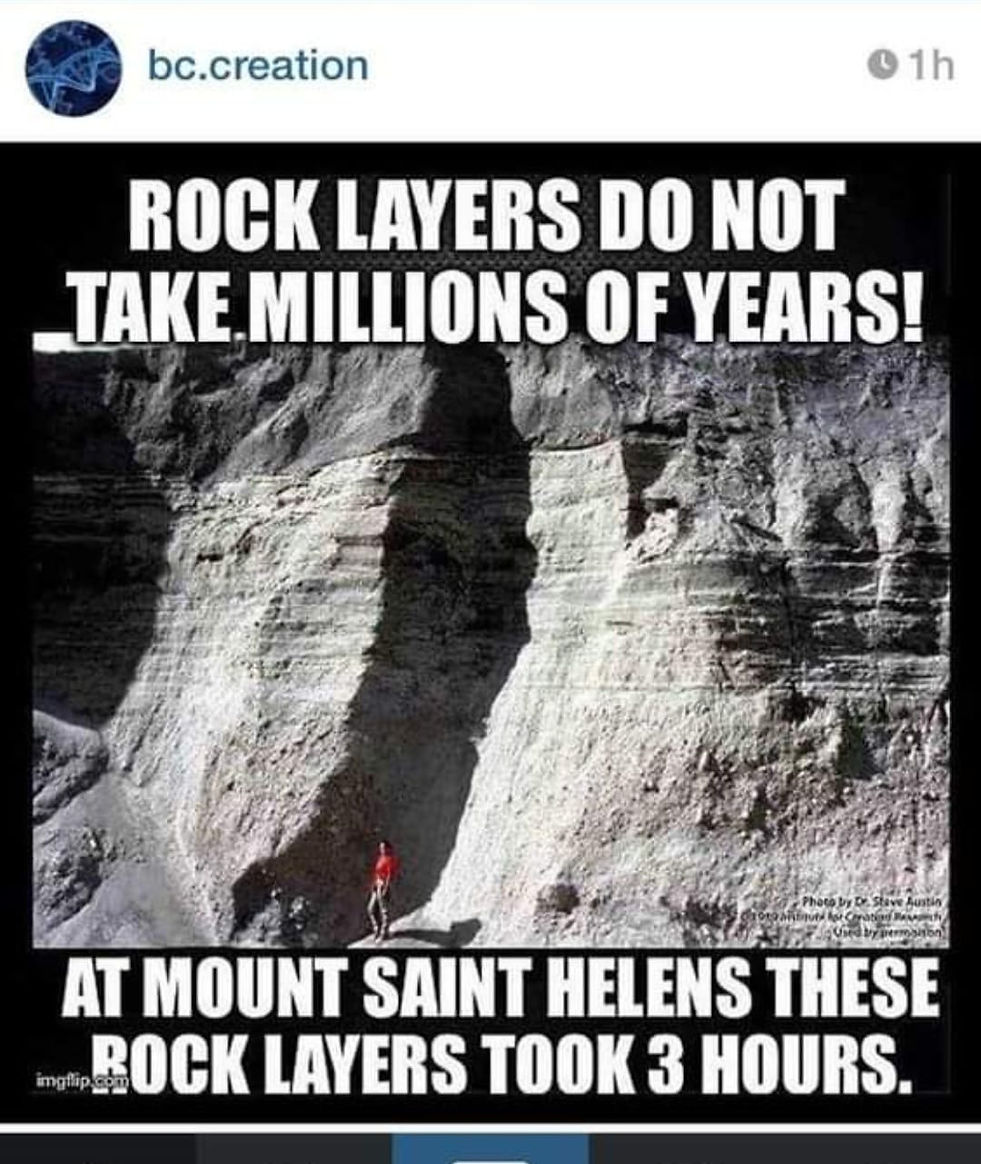
So what is the problem with this headline? In context you know this took 3 hours but without that context you have to figure out what happened forensically. Of course the posters of this are also unaware that impact can produce this same effect as a pile up of impact ash. Look how it appears to have an unconformity. Yes that is a change in the event layering but from the same event. Now that is interesting.

Time - Notice there is no time in the equation E= mc^2. Time is only a part of motion. And it is not linear. Time exist relative to how much motion/event occurs. This geology chart attempts to makes what is not linear into that which is. Days and years were not consistent over the course of this scale. Periods like the early bombardment are not a similar period to the other periods, a separate event type therefore not in the same scale. March 26, 2024.

8 February 2025 Arkeonews. 1.5 Million-Year-Old Hand Axes and Seven Paleolithic Sites Discovered in Iraq’s Western Desert.
One of the scientific research discovered hand tools, with many stone tools and production residues visible on the surface in the background, Iraqi desert. Credit: University of Brussels.
You can't help but notice here that this is the biblical area of the Garden of Eden. While we are told man came from Africa it seems that Africa and the middle east were connected and easier to travel than today. Also this brings up the idea of cycles of environment change and cycles of these human developments. Tool invention could occur, be lost and re invented again. Feb. 8, 2025.
